Capital Structure Decisions Include Determining
Capital letter Structure
Financing avails with debt and equity
What is Majuscule Structure?
Majuscule construction refers to the amount of debt and/or equity employed by a firm to fund its operations and finance its assets. A firm'southward capital structure is typically expressed as a debt-to-equity or debt-to-uppercase ratio.
Debt and disinterestedness capital are used to fund a business organisation'southward operations, capital expenditures, acquisitions, and other investments. There are tradeoffs firms have to make when they decide whether to use debt or equity to finance operations, and managers will residuum the two to find the optimal capital structure.
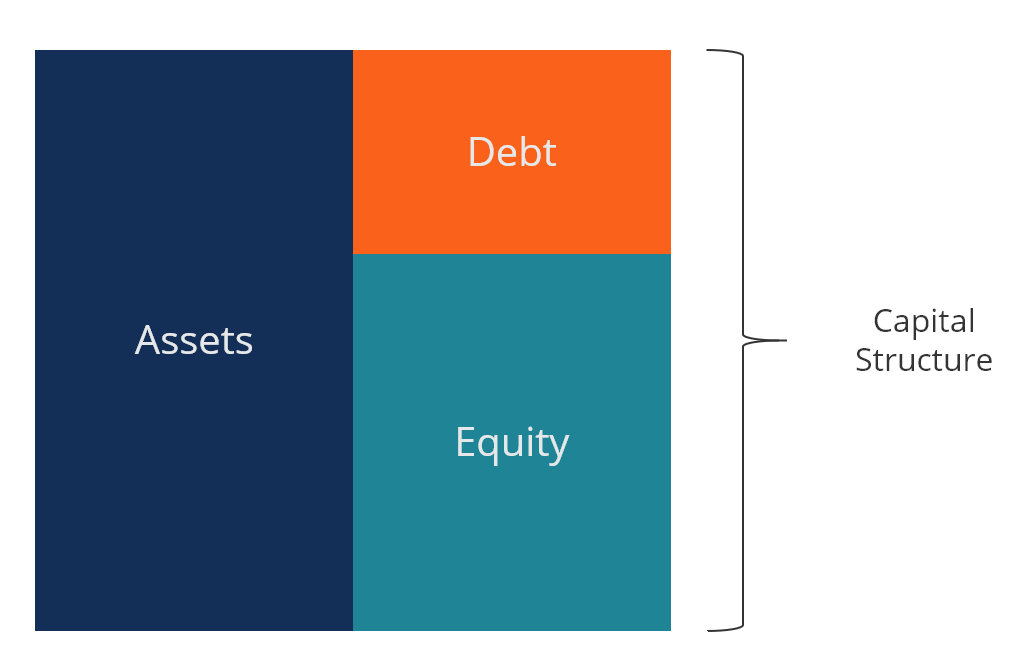
Image from CFI's Free Corporate Finance 101 Grade.
Optimal capital structure
The optimal capital construction of a firm is often defined as the proportion of debt and disinterestedness that results in the lowest weighted average cost of capital letter (WACC) for the firm. This technical definition is not e'er used in practice, and firms often have a strategic or philosophical view of what the platonic structure should be.
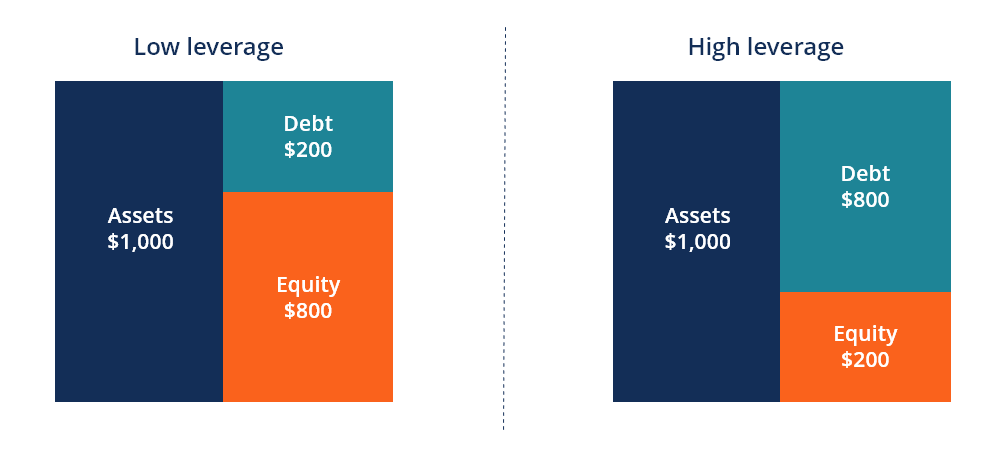
In order to optimize the structure, a firm can issue either more debt or equity. The new capital that'due south acquired may be used to invest in new assets or may exist used to repurchase debt/equity that's currently outstanding, as a form of recapitalization.
Dynamics of debt and equity
Below is an analogy of the dynamics between debt and equity from the view of investors and the firm.
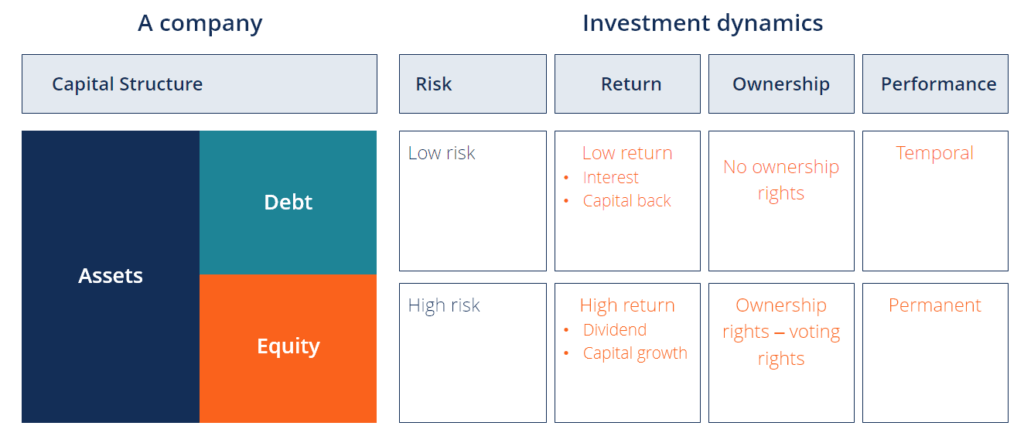
Debt investors have less risk because they have the first merits on the assets of the business concern in the event of bankruptcy. For this reason, they accept a lower rate of return and, thus, the house has a lower toll of majuscule when it issues debt compared to equity.
Equity investors take more take chances, as they only receive the residual value after debt investors have been repaid. In exchange for this take chances, investors expect a higher rate of return and, therefore, the unsaid cost of equity is greater than that of debt.
Cost of capital
A firm'southward total cost of capital is a weighted average of the toll of equity and the cost of debt, known as the weighted average toll of capital (WACC).
The formula is equal to:
WACC = (E/V x Re) + ((D/Five x Rd) x (one – T))
Where:
Eastward = market value of the firm's equity (market cap)
D = market value of the house'due south debt
V = full value of capital (equity plus debt)
E/Five = per centum of majuscule that is disinterestedness
D/V = percentage of upper-case letter that is debt
Re = cost of equity (required rate of render)
Rd = cost of debt (yield to maturity on existing debt)
T = tax rate
To learn more, cheque out CFI's business valuation course or Gratuitous intro to corporate finance course.
Capital letter structure by manufacture
Upper-case letter structures can vary significantly by industry. Cyclical industries like mining are often not suitable for debt, equally their cash menses profiles can be unpredictable and at that place is as well much doubt near their power to repay the debt.
Other industries, like cyberbanking and insurance, use huge amounts of leverage and their business models require big amounts of debt.
Private companies may have a harder time using debt over equity, particularly small businesses which are required to have personal guarantees from their owners.
How to recapitalize a business
A firm that decides they should optimize their capital letter structure by changing the mix of debt and equity has a few options to effect this alter.
Methods of recapitalization include:
- Issue debt and repurchase equity
- Issue debt and pay a large dividend to disinterestedness investors
- Effect equity and repay debt
Each of these three methods tin can be an constructive way of recapitalizing the business.
In the first approach, the firm borrows money by issuing debt and then uses all of the majuscule to repurchase shares from its disinterestedness investors. This has the result of increasing the amount of debt and decreasing the corporeality of equity on the balance sheet.
In the 2d approach, the house will borrow coin (i.e., consequence debt) and utilize that money to pay a one-time special dividend, which has the consequence of reducing the value of equity by the value of the divided. This is another method of increasing debt and reducing equity.
In the third approach, the firm moves in the opposite direction and bug equity by selling new shares, then takes the money and uses it to repay debt. Since equity is costlier than debt, this approach is non desirable and oft only done when a business firm is overleveraged and badly needs to reduce its debt.
Tradeoffs between debt and equity
At that place are many tradeoffs that owners and managers of firms have to consider when determining their capital structure. Below are some of the tradeoffs that should exist considered.
Pros and cons of equity:
- No interest payments
- No mandatory fixed payments (dividends are discretionary)
- No maturity dates (no capital repayment)
- Has ownership and control over the business
- Has voting rights (typically)
- Has a loftier implied price of capital
- Expects a loftier rate of render (dividends and upper-case letter appreciation)
- Has terminal merits on the house's assets in the event of liquidation
- Provides maximum operational flexibility
Pros and cons of debt:
- Has interest payments (typically)
- Has a fixed repayment schedule
- Has showtime merits on the firm's assets in the outcome of liquidation
- Requires covenants and financial performance metrics that must be met
- Contains restrictions on operational flexibility
- Has a lower price than equity
- Expects a lower rate of return than equity
Video Explanation of Uppercase Structure
Watch this brusk video to quickly empathize the master concepts covered in this guide, including the definition of capital structure, what is the optimal capital structure, and the calculation of the weighted average cost of capital (WACC).
Capital structure in mergers and acquisitions (M&A)
When firms execute mergers and acquisitions, the capital construction of the combined entities tin oftentimes undergo a major change. Their resulting structure will depend on many factors, including the class of the consideration provided to the target (cash vs shares) and whether existing debt for both companies is left in place or non.
For example, if Elephant Inc. decides to acquire Squirrel Co. using its own shares as the grade of consideration, it will increment the value of equity capital on its balance canvass. If, nevertheless, Elephant Inc. uses cash (which is financed with debt) to acquire Squirrel Co., information technology will have increased the corporeality of debt on its balance canvass.
Determining the pro forma capital structure of the combined entity is a major part of G&A financial modeling. The screenshot below shows how two companies are combined and recapitalized to produce an entirely new balance sail.

To learn more, check out CFI'due south 1000&A financial modeling course.
Leveraged buyouts
In a leveraged buyout (LBO) transaction, a firm will take on pregnant leverage to finance the acquisition. This practice is normally performed by individual equity firms seeking to invest the smallest possible amount of equity and finance the balance with borrowed funds.
The prototype below demonstrates how the use of leverage can significantly increment equity returns as the debt is paid off over fourth dimension.
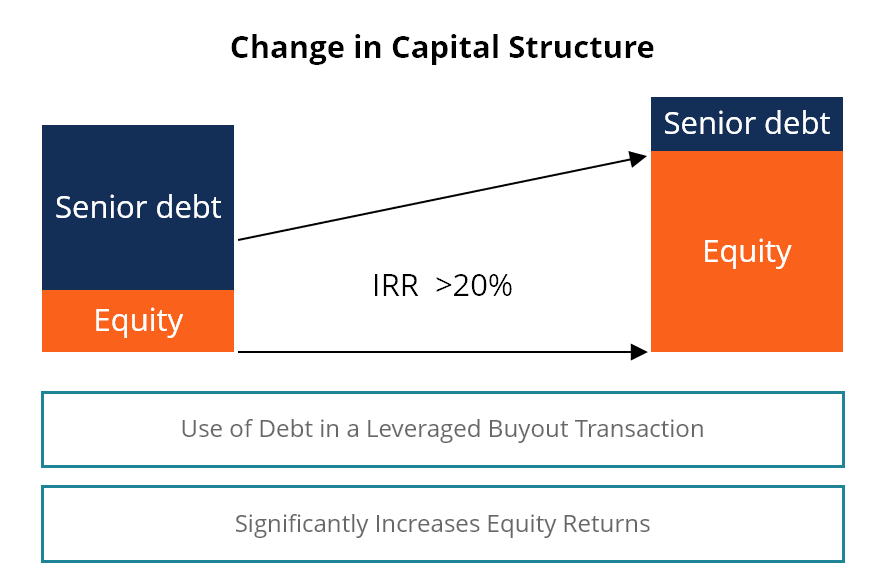
Learn more near LBO transactions and why private equity firms often employ this strategy.
Additional capital structure resources
Thank you for reading this guide and overview of majuscule structures and the important considerations that owners, managers, and investors have to take into account. To go on learning and advancing your career, these additional CFI resources volition be a big help:
- WACC Guide
- Corporate Finance Overview
- Financial Modeling Guide
- DCF Modeling Guide
Capital Structure Decisions Include Determining,
Source: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/finance/capital-structure-overview/
Posted by: covingtonalivink1991.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Capital Structure Decisions Include Determining"
Post a Comment